Three-Agent Collaboration, with message Routing¶
Script in langroid-examples
A full working example for the material in this section is
in the three-agent-chat-num-router.py script in the langroid-examples repo:
examples/quick-start/three-agent-chat-num-router.py.
Let's change the number game from the three agent chat example slightly.
In that example, when the even_agent's LLM receives an odd number,
it responds with DO-NOT-KNOW, and similarly for the odd_agent when it
receives an even number. The step() method of the repeater_task
considers DO-NOT-KNOW to be an invalid response and continues to
look for a valid response from any remaining sub-tasks.
Thus there was no need for the processor_agent to specify who should handle
the current number.
But what if there is a scenario where the even_agent and odd_agent
might return a legit but "wrong" answer?
In this section we add this twist -- when
the even_agent receives an odd number, it responds with -10, and similarly
for the odd_agent when it receives an even number.
We tell the processor_agent to avoid getting a negative number.
The goal we have set for the processor_agent implies that it
must specify the intended recipient of
the number it is sending.
We can enforce this using a special Langroid Tool,
RecipientTool.
So when setting up the
processor_task we include instructions to use this tool
(whose name is recipient_message, the value of RecipientTool.request):
processor_agent = lr.ChatAgent(config)
processor_task = lr.Task(
processor_agent,
name = "Processor",
system_message="""
You will receive a list of numbers from me (the user).
Your goal is to apply a transformation to each number.
However you do not know how to do this transformation.
You can take the help of two people to perform the
transformation.
If the number is even, send it to EvenHandler,
and if it is odd, send it to OddHandler.
IMPORTANT: send the numbers ONE AT A TIME
The handlers will transform the number and give you a new number.
If you send it to the wrong person, you will receive a negative value.
Your aim is to never get a negative number, so you must
clearly specify who you are sending the number to, using the
`recipient_message` tool/function-call, where the `content` field
is the number you want to send, and the `recipient` field is the name
of the intended recipient, either "EvenHandler" or "OddHandler".
Once all numbers in the given list have been transformed,
say DONE and show me the result.
Start by asking me for the list of numbers.
""",
llm_delegate=True,
single_round=False,
)
To enable the processor_agent to use this tool, we must enable it:
The rest of the code remains the same as in the previous section,
i.e., we simply add the two handler tasks
as sub-tasks of the processor_task, like this:
One of the benefits of using the RecipientTool is that it contains
mechanisms to remind the LLM to specify a recipient for its message,
when it forgets to do so (this does happen once in a while, even with GPT-4).
Feel free to try the working example script
three-agent-chat-num-router.py in the
langroid-examples repo:
examples/quick-start/three-agent-chat-num-router.py:
Below is screenshot of what this might look like, using the OpenAI function-calling
mechanism with the recipient_message tool:
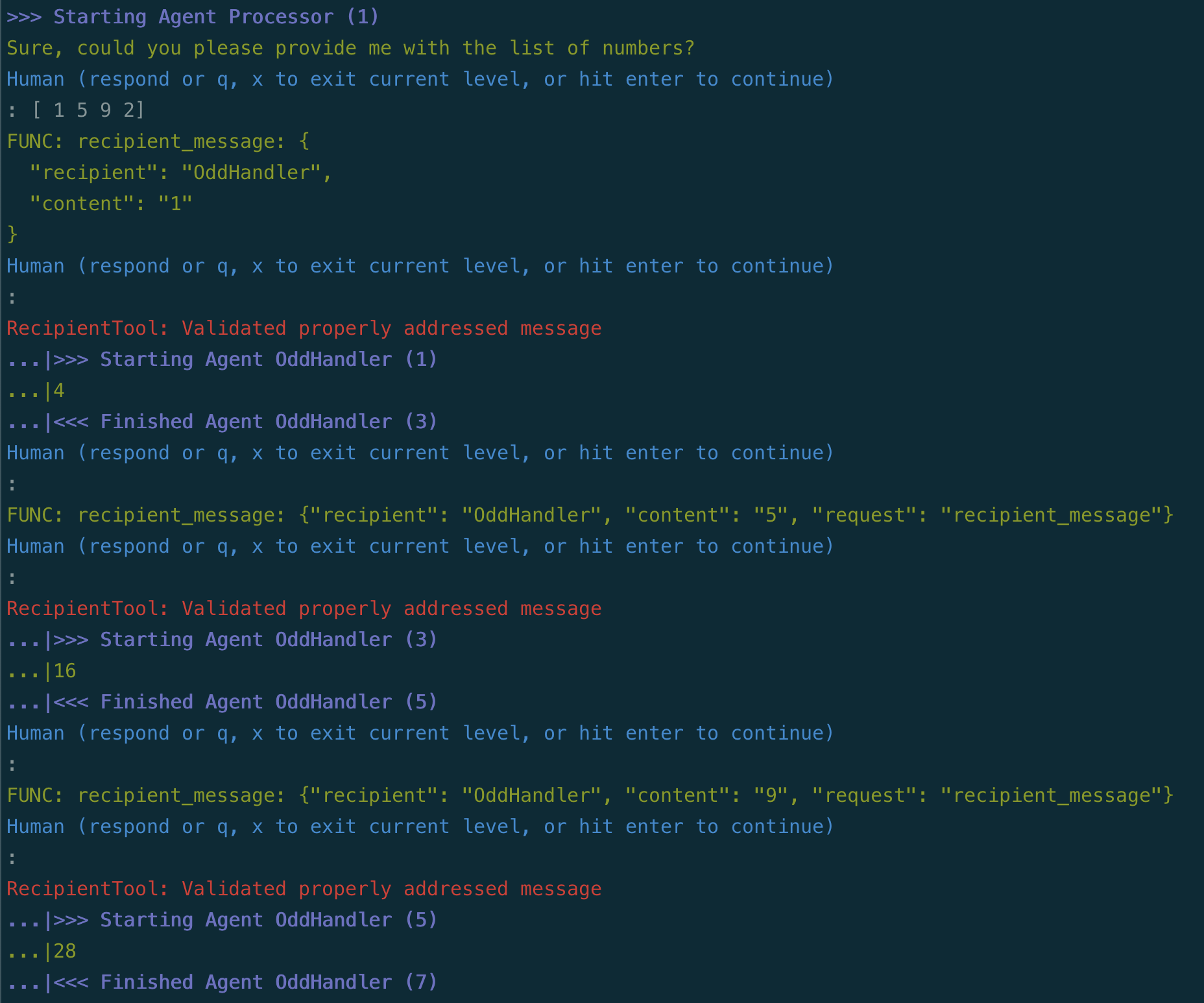
And here is what it looks like using Langroid's built-in tools mechanism (use the -t option when running the script):
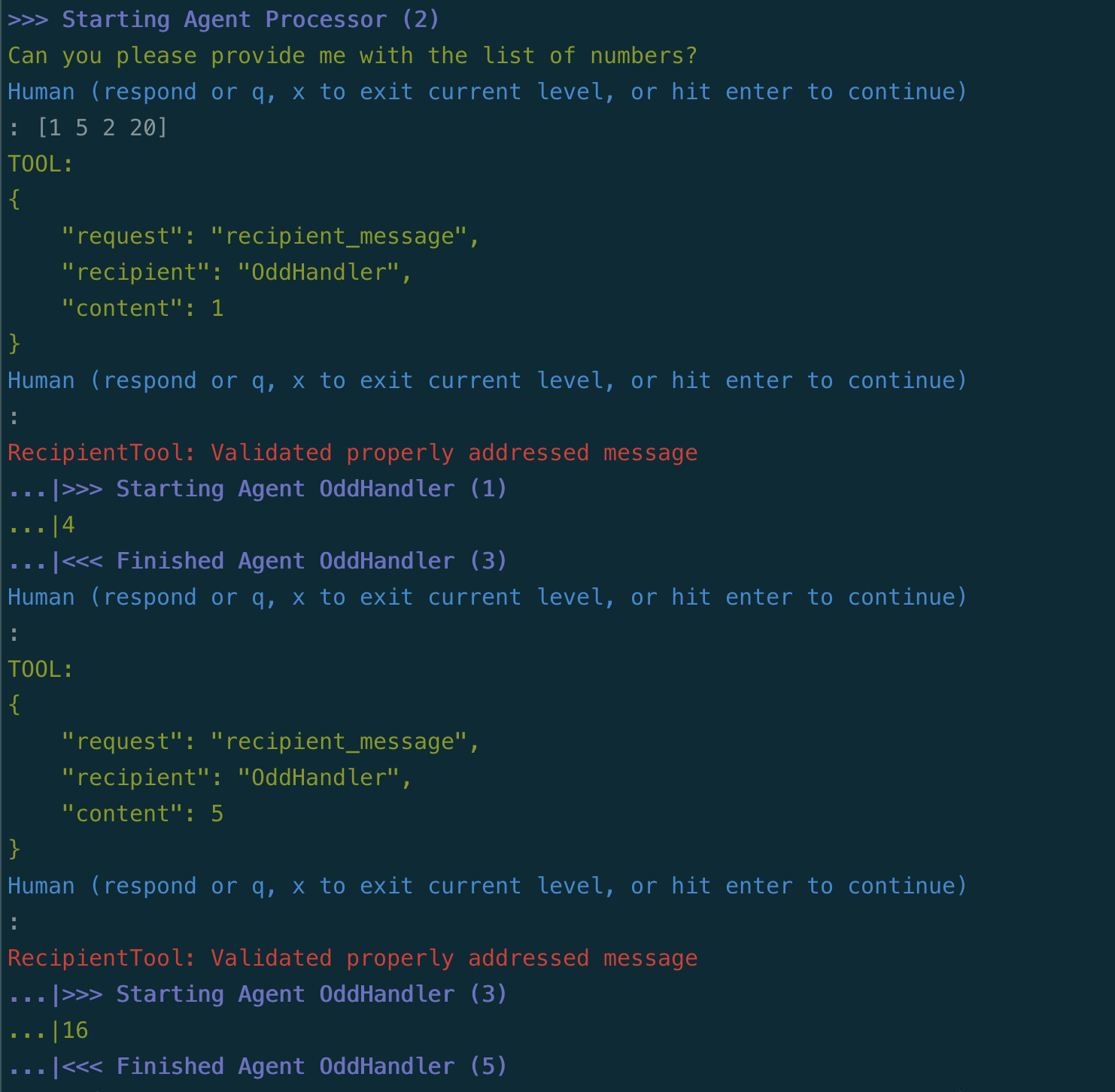
And here is what it looks like using
Next steps¶
In the next section you will learn how to use Langroid with external documents.